top of page

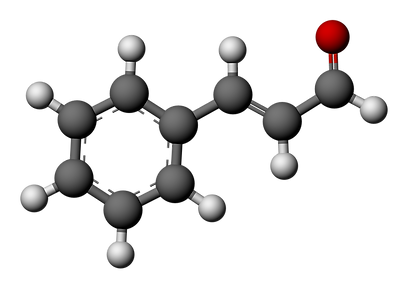
Cinnamaldehyde
Extracted from the bark of Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Cinnamomum cassia, and Cinnamomum camphor, cinnamaldehyde is native to Sri Lanka and India. Its primary use is as a food additive, and is now cultivated in Brazil, Jamaica, and Mauritius.
-
Compound type: organic (aromatic aldehyde)
-
Naturally occurring state: liquid (described as yellowish, oily)
-
Molar mass: 132.16 g/mol
-
Melting point: -7.5ºC
-
Boiling point: 246ºC
-
An aromatic compound (has an "aromatic ring" chemical structure based on that of benzene, C6H6); has a partially cyclic shape
-
Solubility: soluble in...
-
water (slightly)
-
alcohol
-
ether
-
chloroform
-
-
Also known as...
-
Cinnamic aldehyde
-
3-phenyl-2-propenal
-
Cinnamyl aldehyde
-
Phenylalacrolein
-
Cinnamal
-
Trans-cinnamaldehyde
-

Molecular Formula: C9H8O
Structural Formula: C6H5CH=CHCHO
bottom of page